Quote:
In Pyro, we learn thru chemistry that components break down into useless compositions in say 100 years or so, including the BP we make, so whats the diff here?
Or are we doing something to it when we make it makes it last longer? or maybe how it is stored? or.....
|
I don't know about the lifetime of Black Powder other than I have heard that as long as it is kept dry it is as explosive as the day it left the factory.
Smokeless powders are entirely different. Their primary constituent is nitrocellulose. Insensitive munitions experts know that nitrocellulose is the primary constituent in most "propellants", be that cannon powder, rocket motors, or small arms ammunition. The different propellants are all chemically similiar and are all lumped under the names "smokless propellants" in the literature.
Nitrocellulose decomposes through the reduction-oxidation process. Called Redox. The expert said “The molecular stability of the functional groups on the organic chain determine the life time of the nitrocellulose molecule.” All ionic compounds, water is the main offender because it is always in air, react with those bonds and accelerates the deterioration of the powder.
The bottom line is that nitrocellulose is a high energy molecule that wants to become a low energy molecule.
Heat accelerates the deterioration/decomposition of powder and the rate is directly proportional to the Arrhenius equation. If you read in the Insensitive munitions literature, you will see that they use high temperature to accelerate aging of smokeless propellants.
ROLE OF DIPHENYLAMINE AS A STABILIZER IN PROPELLANTS;
ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY OF DIPHENYLAMINE IN PROPELLANTS
Quote:
Nitrocellulose-base propellants are essentially unstable materials
that decompose on aging with the evolution of oxides of nitrogen. The
decomposition is autocatalytic and can lead to failure of the ammunition or disastrous explosions.
|
http://www.dtic.mil/dtic/tr/fulltext/u2/783499.pdf
Heat, as you can see in the report, will age gunpowder
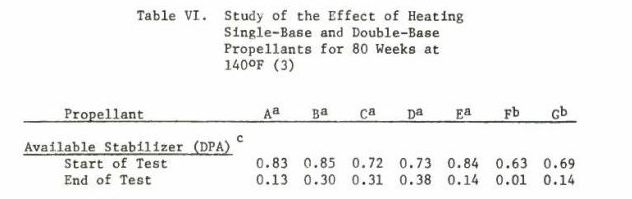
Combustion pressures will rise after high temperature storage.
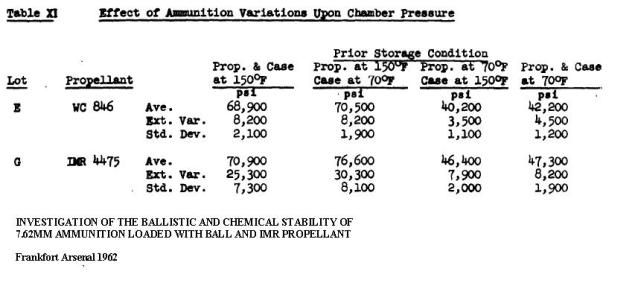
INVESTIGATION OF THE BALLISTIC AND CHEMICAL STABILITY OF 7.62MM AMMUNITION LOADED WITH BALL AND IMR PROPELLANT
Frankfort Arsenal 1962
3. Effects of Accelerated Storage Propellant and Primer Performance
To determine the effect of accelerated isothermal storage upon propellant and primer performance, sixty cartridges from each of lots E (WC 846) and G (R 1475) were removed from 150F storage after 26 and 42 weeks, respectively. The bullets were then removed from half the cartridges of each lot and from an equal number of each lot previously stored at 70F. The propellants were then interchanged, the bullets re-inserted, and the cases recrimped. Thus, four variations of stored components were obtained with each lot.
Chamber pressures yielded by ammunition incorporating these four variations were as follows. These values represent averages of 20 firings.
Double based powders have a reduced lifetime compared with single base. Double based powders have nitroglycerin (NG) in the grain. Nitroglycerine remains a liquid and it migrates within the grain to react with the NO bonds on the nitrocellulose, increasing the rate of reduction-oxidation reaction. All ionic compounds react with those bonds and accelerate the deterioration of the powder. Rust is bad as ferric oxide is ionic. Water is polar covalent ion and is ever present in the air.
Section from the Propellant Management Guide:
Stabilizers are chemical ingredients added to propellant at time of manufacture to
decrease the rate of propellant degradation and reduce the probability of auto ignition during its expected useful life.
As nitrocellulose-based propellants decompose, they release nitrogen oxides. If the nitrogen oxides are left free to react in the propellant, they can react with the nitrate ester, causing further decomposition and additional release of nitrogen oxides. The reaction between the nitrate ester and the nitrogen oxides is exothermic (i.e., the reaction produces heat). Heat increases the rate of propellant decomposition. More importantly, the exothermic nature of the reaction creates a problem if sufficient heat is generated to initiate combustion. Chemical additives, referred to as stabilizers, are added to propellant formulations to react with free nitrogen oxides to prevent their attack on the nitrate esters in the propellant. The stabilizers are scavengers that act rather like sponges, and once they become “saturated” they are no longer able to remove nitrogen oxides from the propellant. Self-heating of the propellant can occur unabated at the “saturation” point without the ameliorating effect of the stabilizer. Once begun, the self-heating may become sufficient to cause auto ignition.
The Armed Forces have stockpile surveillance programs but each Service does theirs a little differently. If you want to see all the different tests the military uses to determine propellant characteristics, look at Mils Std 286 Propellants, Solid: Sampling, Examination and Testing to be found at
https://assist.daps.dla.mil/quicksearch/.
If you look, you will find aging tests. One common test is for powder to be kept at 65 C (150 F) until it fumes. It if fumes within 30 days it is checked for stabilizer or scrapped.
The Navy expert told me a few ways the Navy samples its powders and propellants. If the powder is outgassing nitric gas (as determined by change of color of methly violet paper in contact with the powder (Methly Violet test, or Talliani test)), the stuff is tested to see how much stabilizer is left. If the amount is less than or equal to 20%, the lot is scrapped.
Scrapping powders and propellants with this percentage of stabilizer appears to be consistent across all services.
The problem you have with old surplus ammunition is that you don't know how it was stored. If it was stored in hot envirnoments then the stuff is likely to be very bad.
A few years ago Pakistani ammunition got a deserved bad reputation because a number of rifles blew up with the stuff. Most ignorant American's simply applied simplistic thinking, mostly based on stupid assumptions: that Pakistani ammunition blew up because it was made by Pakistani’s. I think it is more reasonable to assume that Pakistani industry made perfectly good ammunition and the stuff sat around long enough, could have been in the hot sun, and Pakistani munitions experts realized this stuff was too dangerous to issue to their troops, but it was perfectly fine to sell to unsuspecting Americans. Who bought it thinking they got a bargin. There is a reason this stuff is cheap.
Pakistani 303 ammunition.